The openSUSE Project is pleased to announce the release of the latest incarnation of openSUSE, with support for 32-bit and 64-bit systems. openSUSE 11.3 is packed with new features and updates including SpiderOak to sync your files across the Internet for free, Rosegarden for free editing of your audio files, improved indexing with Tracker, and updates to Mozilla Firefox, and Thunderbird.
Among these many new features, openSUSE also provides support for netbooks and the Btrfs file system support. Users can expect to see improved hardware support with the 2.6.34 Linux kernel and updated graphics drivers. And support for the next generation of interactive computing for touchscreens like the HP TouchSmart.
openSUSE continues its tradition of delivering the popular KDE, GNOME and Xfce desktop environments, and now also provides the lightweight LXDE desktop environment. With GNOME, you can use the latest 2.30.1 version or take your installation for a drive with a preview of the upcoming GNOME 3.0. Or choose KDE SC 4.4.4 for the latest updates. They all feature the polish and integration that the openSUSE distro has been known for.
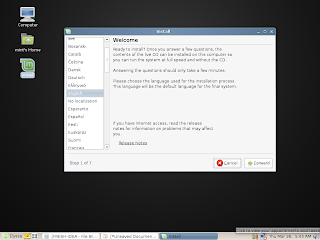
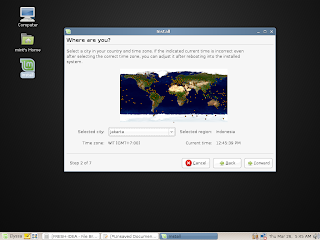
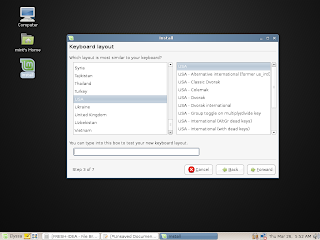
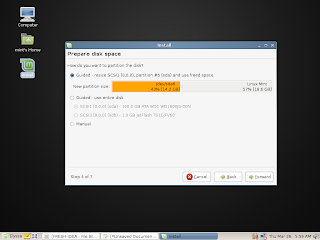
Click the desktop screenshots for a full view or see the complete collection of screenshots here.
- Plasma Desktop on KDE SC 4.4.4
For servers and development platforms, administrators can take full advantage of the new MariaDB and MySQL Cluster services as well as Conntrack to filter network packets for iptables. Developers will appreciate the plethora of tools available at their fingertips with GCC, GDB and Mono and IDEs such as Netbeans, Qt-Creator and many others. This is all on top of the countless libraries available through the openSUSE Build Service (OBS).
Visit our Product Highlights page for a detailed list of new features.
Source : news.opensuse.com